Fortnite is a video game series set in a post-apocalyptic, zombie-infested world. It was created by Epic Games and used the company’s signature Unreal Engine. Currently, Fortnite has two titles: a team survival shooter called Fortnite: Save the World and a single-player game called Fortnite: Battle Royale.
In addition to developing games, Epic Games owns the Unreal game engine and the game store and is actively exploring new forms of gaming for the future. Epic Games has the potential to become one of the most important technology companies in the world, with a core Internet platform that has a huge impact on social life.
Fortnite: Battle Royale is available directly to players for free on PlayStation 4, Xbox One, Microsoft Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and Nintendo Switch, and can be played across multiple platforms, making it one of the most popular games on the planet right now.
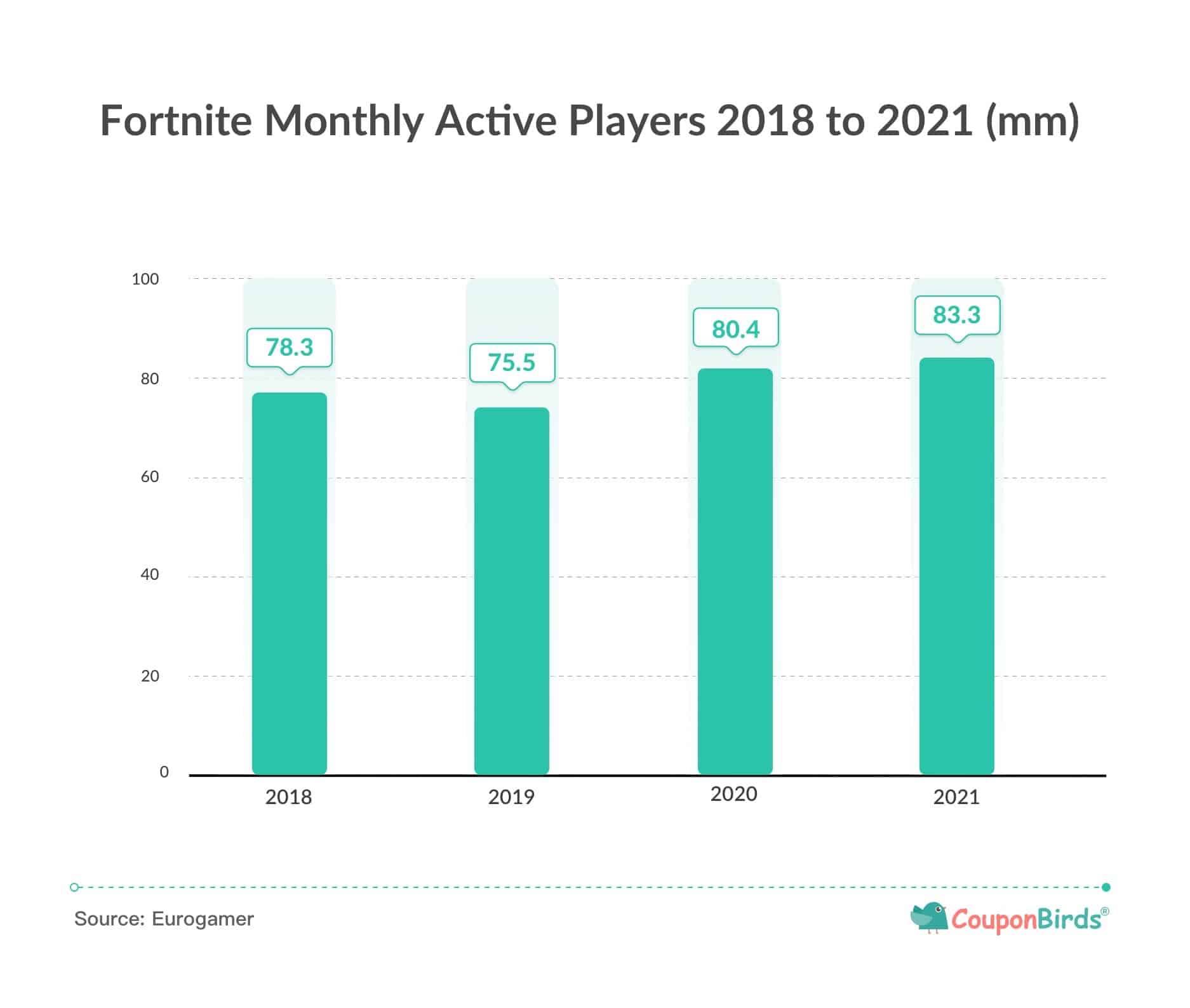
Millions of players have downloaded the game since its launch, generating hundreds of millions of dollars a month for its creators. According to a survey by CouponBirds, Fortnite’s monthly active player base has remained around 80 million. The incredible number of people online makes for incredible profits. Fortnite: Escape brought in $5.4 billion in revenue for Epic in 2018 alone, making it the world’s most profitable game that year.
How did Fortnite achieve so much in such a short time?
Fortnite achieved something previously thought to be almost impossible in the game industry: it was the first game to break through on various console platforms, including XBOX/PS/Switch. Fortnite launched with simultaneous PC/ console/mobile cross-platform connectivity, which is a big deal in the closed gaming ecosystem. This is due to Tim Sweeney and Unreal Engine’s many years in the industry and their contacts and influence.
On the other hand, Fortnite has made a significant model innovation in the F2P premium system with its Battle Pass season ticket subscription model. By most people’s understanding of the F2P free-to-play in-game payment mechanism, it is the treasure chest or the so-called ten-in-a-row model. Treasure chests are a great way to monetize a game on a large scale, but the numerical strength of the paying players affects the game’s balance, and the endless amount of money often makes the game taste bad.
How does Fortnite do it? It goes the other way, using a subscription system generally accepted in Western Internet culture, and differentiates rewards by season. More important is how rewards are earned: each season, users can play for free to earn experience points that can be used to improve their Battle Pass level for the season, and each level has a corresponding reward.
Here’s the kicker: each level of Battle Pass comes with a free bonus, but the main bonus will require users to pay a one-time fee to unlock this season’s Battle Pass before getting it.
The player has actually earned these rewards through the investment of time in the game and needs to pay the convoluted lock to get all of their rewards. This is completely different from the concept of subscription, where before Fortnite, you paid for a subscription to get “access to the game.” In-game rewards can only be earned if the user spends time playing them. In Fortnite, on the other hand, players can play and earn rewards regardless of whether they spend money or not. The rewards that players have spent time earning are displayed in the window, enticing users to spend money to unlock this season’s Battle Pass to get their rewards. The more time the player has to invest, the more tempting it becomes to monetize. The player invests time to value and then pays to monetize that time value into reward value. Also, the rewards of the Fortnite Battle Pass do not affect the strength of the user’s character, and there is no psychological pressure to buy a Battle Pass to improve the character’s stats.
These mechanics combine to create an addictive growth experience that allows Fortnite games to harvest retention and daily active players like crazy. Fortnite’s Battle Pass launched with a whopping 70% pay rate, something every game developer can only dream of. Fortnite’s original Battle Pass payment design was a huge success, followed by many of the world’s biggest games, and almost all of them had an immediate effect on retention and payment.
Not only that, but in Fortnite, users can build, socialize, and interact. Beyond the gaming experience, Fortnite quickly morphed into a social space, connecting the game space with real life. Fortnite is one of the closest systems ecosystems to a “meta-universe” right now. It’s not quite a game anymore, but increasingly social, evolving into a virtual space where custom characters interact. So far, there have been concerts, movie launches, fan meets, and other real-world events held in Fortnite’s virtual environment:
- Marshmello’s first live Fortnite concert in February 2019 was played by more than 10 million players;
- In April 2019, Marvel’s Avengers: Endgame offered a new co-branded interactive mode in Fortnite, where players take on the role of the Avengers as they battle Thanos;
- In December 2019, Star Wars: The Rise of Skywalker held an audience screening at Fortnite, where director JJ Abrams was interviewed;
- In April 2020, American rapper Travis Scott held an immersive concert called Astronomical in Fortnite, which was watched by 17 million people at the same time, causing a viral spread on social media;
- In August 2021, Ariana Grande, a popular American singer, performed five consecutive concerts in Fortnite.

